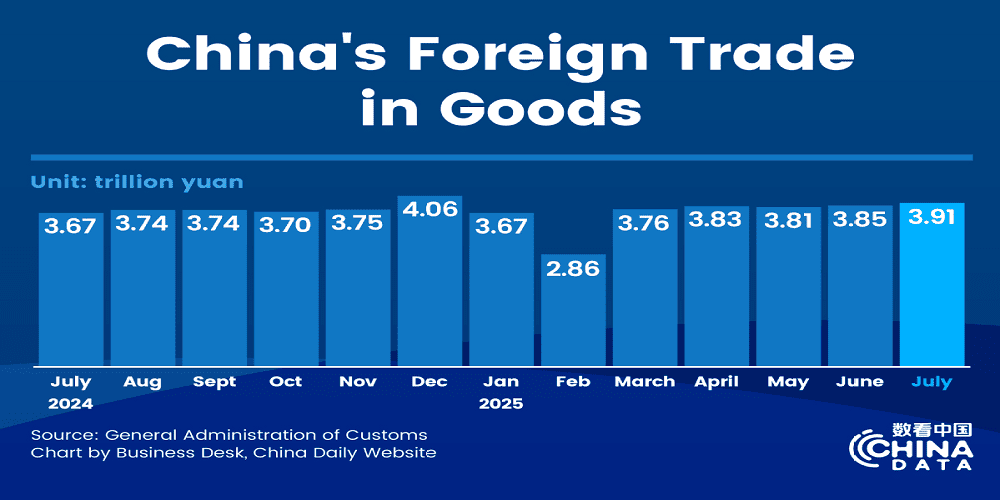
In 2025, China stands at the forefront of a global digital revolution, leveraging data as a cornerstone of its economic and technological strategy. The nation's ambitious vision, encapsulated in the "Digital China" initiative, aims to harness the power of data to drive innovation, enhance governance, and bolster economic growth. This comprehensive analysis delves into China's data landscape in 2025, exploring its policies, infrastructure, economic implications, and the challenges it faces. Launched as part of the 14th Five-Year Plan, the Digital China strategy envisions the creation of a robust digital ecosystem that integrates data across all sectors of society. By 2025, China aims to achieve significant milestones in data infrastructure, governance, and utilization. Key objectives include: Establishing a Unified Data Framework: Implementing standardized data management practices across governmental and private sectors to ensure consistency and reliability. Advancing AI Integration: Promoting the development and application of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Enhancing Cybersecurity: Strengthening data protection measures to safeguard national security and individual privacy. Fostering Innovation: Encouraging the growth of data-driven industries, such as e-commerce, fintech, and smart manufacturing. China's approach to data governance is characterized by a combination of stringent regulations and proactive policy initiatives. Notable developments include: Network Data Security Management Regulation: Effective from January 2025, this regulation aims to standardize data processing activities, emphasizing the protection of personal information and national security Gov.cn. Cross-Border Data Transfer Regulations: Implemented in March 2024, these regulations govern the flow of data across borders, ensuring compliance with domestic laws and international agreements DLA Piper Data Protection. Data Protection Compliance Audits: Starting May 2025, businesses are required to undergo regular audits to assess their adherence to data protection laws, with penalties for non-compliance globalprivacyblog.com. China's investment in AI and big data technologies has led to significant advancements in various sectors: Smart Cities: The deployment of AI-powered systems has transformed urban management, enhancing traffic control, waste management, and public safety. Healthcare: AI algorithms analyze medical data to assist in diagnostics, treatment planning, and drug discovery. Manufacturing: The integration of AI in production lines has optimized processes, reduced waste, and improved product quality. The expansion of data centers and cloud computing infrastructure is pivotal to China's digital strategy: Data Center Growth: China's State Grid Corporation projects a doubling of data center electricity demand from 38 gigawatts in 2020 to over 76 gigawatts by 2025, highlighting the rapid growth of digital infrastructure RAND Corporation. Cloud Services: Major tech companies, including Alibaba and Tencent, have expanded their cloud offerings, providing scalable solutions for businesses and government agencies. To protect its digital assets, China has implemented robust cybersecurity measures: Regulatory Oversight: The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) conducts regular inspections of network and data security practices, focusing on telecommunications and internet enterprises Bird & Bird. Data Protection Laws: The introduction of comprehensive data protection laws in 2025 mandates organizations to implement stringent security protocols and conduct regular compliance audits Mayer Brown. The digital economy has become a significant driver of China's GDP: E-Commerce: Online retail sales of physical goods reached 6.1 trillion yuan in the first half of 2025, accounting for 24.9% of total retail sales National Bureau of Statistics of China. Fintech: The proliferation of digital payment platforms and online lending services has revolutionized the financial sector. Smart Manufacturing: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies has enhanced productivity and competitiveness in the manufacturing sector. The digital transformation has reshaped the labor market: Platform-Based Employment: There has been an increase in platform-based workers, with women and youth representing 53% and 49% of this workforce, respectively The World Bank Documents. Skill Development: The demand for digital skills has surged, prompting educational institutions and training programs to focus on AI, data analytics, and cybersecurity. China's data strategy has implications for its international trade relations: Export Dynamics: In August 2025, China's export growth slowed to 4.4% year-on-year, partly due to ongoing trade tensions with the U.S. and a shift in export destinations Financial Times. Digital Silk Road: China is promoting the "Digital Silk Road" initiative, aiming to enhance digital infrastructure and e-commerce connectivity with partner countries. The extensive collection and utilization of data raise privacy and ethical issues: Personal Information Protection: The definition and handling of sensitive personal information in China differ from other jurisdictions, necessitating careful consideration by businesses operating internationally Privacy Matters. Surveillance: The widespread use of surveillance technologies has sparked debates about individual freedoms and state control. China's emphasis on technological self-reliance presents both opportunities and challenges: Domestic Innovation: Efforts to develop indigenous technologies reduce dependence on foreign entities but require significant investment in research and development. Global Standards: China's approach to data governance may conflict with international norms and standards, potentially complicating cross-border collaborations. The rapid expansion of digital infrastructure has environmental implications: Energy Consumption: The growing demand for data centers contributes to increased energy consumption, raising concerns about sustainability. E-Waste: The lifecycle of digital devices and equipment leads to the generation of electronic waste, necessitating effective recycling and disposal mechanisms. Looking ahead, China's data strategy is poised to evolve: AI Leadership: By 2030, China aims to be the world's primary leader in AI, with multiple technology innovations and personnel training centers datagovhub.elliott.gwu.edu. Digital Governance
No items to display.The Digital China Strategy
Vision and Objectives
Policy and Regulatory Landscape
Data Infrastructure and Technological Advancements
AI and Big Data Integration
Data Centers and Cloud Computing
Cybersecurity Measures
Economic Implications
Digital Economy Growth
Employment and Labor Market
Trade and Global Influence
Challenges and Considerations
Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Technological Sovereignty
Environmental Impact
Future Outlook

Leave A Comment
0 Comment